Diabetes is one of the most critical health challenges in Asia, with millions of patients requiring long-term management. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, treatments, prevention methods, natural remedies, and leading diabetes care centers across the region.
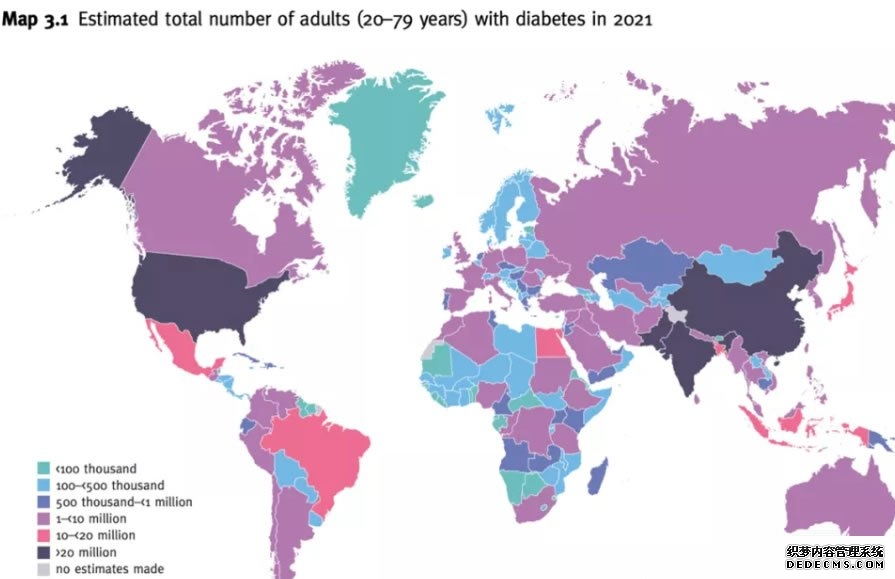
Diabetes has become a major health burden in Asia, where rapid urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, and dietary changes have caused a dramatic increase in cases. The International Diabetes Federation estimates that Asia accounts for nearly half of all global diabetes patients. Countries such as China, India, and Indonesia have witnessed exponential growth in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes cases, while wealthier regions such as Singapore and Japan face unique challenges related to aging populations and lifestyle habits.
Understanding Diabetes in Asia
Diabetes is primarily categorized into type 1 (autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells) and type 2 (insulin resistance). While type 1 diabetes is less common, type 2 dominates across Asia due to lifestyle and genetic predisposition.
Risk factors prevalent in Asia include:
- High carbohydrate diets with refined rice and processed foods
- Low physical activity in urban areas
- Obesity and metabolic syndrome
- Limited access to early screening and diagnosis in rural regions
The disease’s impact extends beyond individual patients, straining healthcare systems and national economies. Diabetes complications—heart disease, kidney failure, and blindness—lead to reduced workforce productivity and increased healthcare expenditure.
Latest Medical Treatments
Modern diabetes care has advanced considerably. Traditional reliance on oral medications like metformin has now been complemented by innovative therapies:
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: Effective in lowering blood sugar while aiding weight loss.
- SGLT2 inhibitors: Beneficial for patients with both diabetes and heart or kidney disease.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): Devices like Freestyle Libre and Dexcom enable real-time tracking.
- Insulin pumps: Miniaturized pumps provide consistent delivery and reduce daily burden.
In Asia, adoption of these therapies varies. Wealthier nations such as Singapore and Japan offer wide access, while in India and Indonesia, affordability remains a key barrier. Governments are beginning to subsidize advanced therapies to improve outcomes.
Preventive Care and Lifestyle Management
Prevention is the most cost-effective strategy. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and routine screening can reduce the onset of type 2 diabetes. In many Asian cultures, rice remains the staple, but portion control, high-fiber alternatives, and plant-based diets are gaining acceptance.
Exercise programs focusing on walking, yoga, and tai chi are being recommended as culturally acceptable fitness routines. Governments are promoting workplace wellness programs and public health campaigns to reduce sugar consumption.
Natural Remedies and Traditional Approaches
Natural remedies are deeply rooted in Asian traditions. While not substitutes for medical care, they can complement treatment:
- Bitter melon (Momordica charantia): Believed to help regulate blood sugar.
- Cinnamon: Studied for potential insulin-sensitizing properties.
- Ayurvedic and Traditional Chinese Medicine herbs: Used for centuries to manage symptoms.
- Mindfulness and stress reduction: Meditation and breathing exercises support lifestyle management.
It is crucial to combine these remedies with evidence-based treatments and under medical supervision.
Leading Diabetes Care Centers in Asia
Several hospitals and research centers have emerged as leaders in diabetes care:
- National University Hospital, Singapore
- Apollo Hospitals, India
- Peking Union Medical College Hospital, China
- St. Luke’s International Hospital, Japan
These centers provide multidisciplinary care including endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators. Many also participate in global research trials.
Conclusion
Diabetes care in Asia is at a crossroads. The disease is spreading rapidly, yet advances in medical treatment, preventive measures, and integration of traditional remedies offer hope. Patients must adopt a proactive role—balancing modern medicine with lifestyle changes—to live healthier, longer lives.
diabetes care Asia, best diabetes treatment, managing diabetes naturally